Coksartrosis- This is arthritis in the hip joint.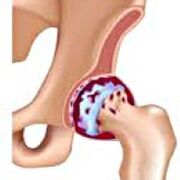 It gradually develops into several years, easy to develop, and can be both one aspect or both.It is accompanied by pain and limitations of joint movement.In the later stage, atrophy of the hip muscles and shortening of the limbs were observed.Establish a diagnosis based on clinical symptoms and radiographic results.In the early stages of gulf neuropathy, conservative treatment.With joint destruction, especially in young and middle-aged patients, surgery (internal main mindset) is pointed out.
It gradually develops into several years, easy to develop, and can be both one aspect or both.It is accompanied by pain and limitations of joint movement.In the later stage, atrophy of the hip muscles and shortening of the limbs were observed.Establish a diagnosis based on clinical symptoms and radiographic results.In the early stages of gulf neuropathy, conservative treatment.With joint destruction, especially in young and middle-aged patients, surgery (internal main mindset) is pointed out.
General information
COKSARTROSIS (Osteoarthritis or hip deformed arthritis) is a degenerative disease.It is usually developed at the age of 40 and above.This may be the result of various injuries and joint diseases.Sometimes it happens for obvious reasons.Coksartrosis is characterized by a progressive course.In the early stages, conservative treatments were used.In the later stages, joint function can only be restored.
In orthopedics and trauma, competitive arthritis is one of the most common arthritis.The high frequency of its development is due to the significant load on the hip joint and the widespread prevalence of congenital pathology-articular dysplasia.Women suffer more frequently than men.
The reason for Coksartrosis
The main (produced by other diseases) and secondary (produced by other diseases) of the hip joint are distinguished.
Secondary coksartrosis may be the result of the following diseases:
- Hip dysplasia.
- Born thigh dislocation.
- Pertes' disease.
- Sterile necrosis of the thigh.
- Infectious lesions and inflammatory processes (e.g., hip arthritis).
- Injury (traumatic dislocation, hip fracture, pelvic fracture).
Coksartrosos can be one aspect or two-sided.Concomitant lesions of the spine (osteochondrosis) and knee joints (promoting myocardial joints) are often observed.
Risk factors
Factors that increase the likelihood of gulf nerve development include:
- Constantly increase joint load.Most people are often observed in overweight athletes.
- Circulatory system diseases, hormone changes, metabolic disorders.
- Spine pathology (cerebrospinal, scoliosis) or stop (flat feet).
- Old age and old age.
- A sedentary lifestyle.
Coksartrosis itself is not inherited.However, children can inherit certain characteristics from their parents (metabolic diseases, bone structural features and weaknesses in cartilage).Therefore, in the presence of competitive blood relatives, the likelihood of disease development is slightly increased.
Pat technique
The hip joint is formed by two bones: the ileum and the femur.The head of the thigh is indicated by the acetabulum of the leaf bone, forming a special "hinge".During the movement, the acetabular remains motionless and the femoral head moves in all directions, ensuring flexion, extension, abduction, bringing and rotating the hips.
During the movement, the joint surfaces of the bones slide unhindered relative to each other due to the smooth, elastic and durable clear cartilage covering the rotating cavity and the thigh head.Furthermore, hyacinth cartilage performs shocking functions and participates in the redistribution of loads during movement and walking.
In the joint cavity, there is a small amount of joint fluid, which plays a lubricating role and provides nutrition for clear cartilage.The joint is surrounded by dense and strong capsules.Above the capsule are large femur and hip muscles that provide movement in the joints, as well as hyaluronic cartilage, which is also a shock absorber that protects the joints from unsuccessful movement.
As carbon dioxide changes, joint fluid becomes thicker and stickier.The surface of the clear cartilage is dry, losing its smoothness and covering the cracks.Due to the roughness generated, cartilage during exercise can be continuously injured, which can cause them to thin and exacerbate pathological changes in the joints.As carbon dioxide progresses, bones begin to deform, "adapting" to increase stress.Metabolism in joints is deteriorating.In the later stages of Grey Neurosis, severe atrophy of the sore muscle was observed.
Competitive symptoms
The main symptoms of the disease include pain in the joints, groin area, thighs and knees.Similarly, as heel movement, the stiffness of the movement and joint stiffness, gait disturbance, laxation, atrophy of the hip muscles, and shortening of the limbs on the lesion side were observed.One feature of Coksartrosis is the limitations on kidnapping (for example, it is difficult for patients to try to sit in a chair).The presence of certain signs and their severity depends on the stage of coronary heart disease.The first and most persistent symptom is pain.
existLevel 1 COKSARTROSISPatients complain of periodic pain, which occurs after physical exercise (running or long walking).Pain is located in the joints with less thighs or knees.After a break, it usually disappears.The gait in the first-level competition was not ruptured, the movement was completely preserved, and there was no muscle atrophy.
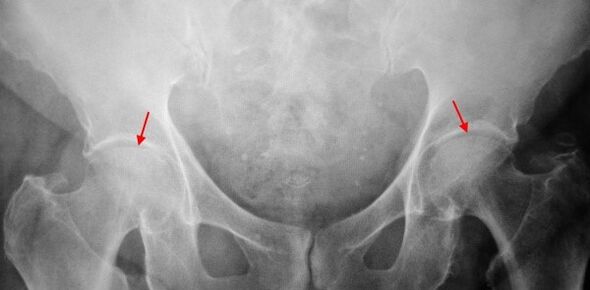
On X-rays of patients with primary binary bovine car, slight changes were identified: uneven stenosis of joint spaces, and the growth of bones around the outer or internal edge of the acetabular without changes in the head and neck of the femoral head.
existCoksartrosis 2 degreesThe pain becomes more intense and often occurs in a static state, radiating into the thighs and groin.After major physical exercise, patients with Coksartrososis began to move.Reduced amount of movement in the joint: The abduction and internal rotation of the thigh are limited.
Binary images used in X-ray images for secondary binary binary images, identifying obvious uneven stenosis (more than normal height) in joint gaps.The femoral head moves upward to some extent, deformation and size increase, and the contour becomes uneven.The bone growth of the sacrificial neuropathy appears not only inside, but also on the outer edge of the acetabular and then goes out of the cartilage.
existCoksartrosis 3 degreesThe pain becomes constant, not only during the day but also at night.Walking is difficult, and while moving, patients with Coksartrosis are forced to use sugar cane.The amount of exercise in the joints is greatly limited, and muscles in the hips, buttocks and calf are atrophy.The weakness of the thigh removing muscles is the cause of pelvic deviation in the anterior plane and shortens the limbs on the painful side.To compensate for the shortening, patients with Coksarrosis while walking lean their bodies in the direction of pain.Therefore, the center of gravity moves and the load on the sore joint increases dramatically.
Regarding the third degree of transverse bow radiography, the sharp narrowing of the joint gap, the significant expansion of the thigh head and multiple bone growth were detected.
diagnosis
Competitive diagnosis is based on clinical signs and data from other studies, mainly XhRography.In many cases, X-rays can establish not only the extent of corona but also the cause of it.Thus, for example, an increase in the cervical cross-sectional angle, acetabular scene and flattening suggest that changes in the proximal part of the femur suggest that Coksartrosis is the result of Pertes disease or young epidermal decomposition.Changes can also be detected on X-rays of patients with laparotomy, indicating injury.
Other auxiliary diagnostic methods can be used, CT and MRI can be used.Computed tomography allows you to study pathological changes in detail through bone structure, while magnetic resonance imaging provides an opportunity to evaluate disease through soft tissue.
Differential diagnosis
First, competition should be distinguished from renal conjunctiva (osteoarthritis of the knee joint) and spinal osteocartilage degeneration.Muscle atrophy occurs in stages 2 and 3 of the fifty ball connection, causing knee pain, which is usually brighter than the pain in the damaged area.Therefore, because of the patient’s complaints about knee pain, clinical (examination, palpation, determination of exercise volume) studies are studies of the hip joints, and if coxarthrosis is suspected, the patient is directed to radiograph.
Osteochondrosis and some other spinal diseases stimulate the radicular syndrome (compression of nerve roots) can mimic pain through coxarthosis.Unlike cruisers, when squeezing the roots, pain suddenly occurs, after failure of exercise, make sharp turns, lift weights, etc., place it partially in the hips and spread along the back of the thighs.Positive symptoms of tension were detected - When the patient tried to lift his limb, he felt severe pain and lay on his back.Meanwhile, the patient is free to stretch his legs to the side, and in patients with Coksartrosis, the abduction is restricted.It should be kept in mind that osteocartilage and coksartrosis can be observed simultaneously, and therefore, in all cases, a thorough examination of the patient is required.
In addition, COKESARTROSIS is distinguished from Boot Bursite - sterile inflammation in the gluteal attachment area.Unlike cruisers, the disease usually develops rapidly within 1-2 weeks, usually after injuries or major physical exercise.The pain is more intense than Coksartrosis.No limitations of movement and limb shortening were observed.
In some cases, a disease similar to a competitive disease or an atypical course of reactive arthritis can be observed.Unlike cruisers with these diseases, the peak of pain at night falls.Pain syndrome is very intense and may be reduced when walking.The stiffness of the morning is a feature, which occurs immediately after waking up and gradually disappearing within a few hours.
Treatment of Guguan
The treatment of pathology involves trauma scientist orthopedics.The choice of treatment depends on the symptoms and stage of the disease.Conservative treatment was performed during the coronary heart disease stages in stages 1 and 2.During the period of aggravation of carbon dioxide, injection blocks, non-replacement anti-inflammatory drugs (pyroxes, indomethacin, diclofenac, ibuprofen, etc.).It should be remembered that for a long time, the use of drugs from this group was not recommended because they negatively affect internal organs and inhibit the ability of hyacinth cartilage recovery.
To restore damage to cartilage from coksarrosis, a set of cartilage protective agents (chondroitin sulfate, cartilage extract, etc.) funds were used.In order to improve blood circulation and eliminate spasms of small blood vessels, drugs for vasodilation (Zinnarisine, nicotine, benzoyl pentoxide, yellowsulfanominine) are prescribed.Based on these signs, use a muscle relaxant (muscle relaxant).
Using stubborn pain syndrome, patients with coksartrosos can be prescribed using hormone drugs (hydrocortisone, triamcinolone, Metrumor)Treatment with steroids must be carried out with caution.Additionally, using carbon dioxide, local products are used - warming ointments that have no obvious therapeutic effects, but in some cases they relieve muscle cramps and reduce their "distraction" effects and relieve pain.In addition, with the provisions of carbon dioxide (luminescence, ultrasound therapy, laser therapy, UHF, sensitive therapy, magnetic therapy), massage, manual therapy and therapeutic gymnastics.
The diet of coxa disease has no independent therapeutic effect and is only used as a means of weight loss.Losing weight can reduce the load on the hip joint, thereby promoting the process of coagulation.To reduce joint load, the doctor, depending on the level of Coxsa, may recommend walking with a cane or a cane.
In later stages (with 3-grade coronary heart disease), the only effective treatment is to operate - replace damaged joints with intra or endoplants.Depending on the nature of the lesion, a single rod (replace only the thigh head) or two rods (can use the thigh head and the head of the rotating cavity).
After a complete examination under general anesthesia, the operation of the worm in a planned manner was performed in a planned manner.After the operation, antibiotic treatment was performed.The seams were removed within 10-12 days, and the patient was prescribed for outpatient treatment.After the internal worm is irritated, rehabilitation measures must be taken.
In 95% of cases, surgical interventions to replace the joint with coils ensure full recovery of limb function.Patients can work, move actively and even exercise.According to all recommendations, the average service life span of the prosthesis is 15-20 years.Thereafter, a second operation is required to replace the worn endometrial prosthesis.